Top 10 Benefits of Using Laminated Glass in Modern Architecture
In modern architecture, the aesthetic appeal and durability of materials play a crucial role in design and construction. One such material that has gained significant acclaim is laminated glass. According to a report by Transparency Market Research, the global laminated glass market is projected to reach USD 22 billion by 2026, underscoring the increasing adoption of this innovative material in architectural applications. Laminated glass is renowned not only for its safety features but also for its ability to enhance energy efficiency and provide superior sound insulation, contributing to a more sustainable built environment.
Renowned industry expert Dr. Emily Dawson, a senior architect at the International Glass Association, emphasizes its importance: "Laminated glass is revolutionizing how we approach modern structures, offering unparalleled advantages in both safety and design flexibility." This innovative material not only reinforces building integrity but also provides architects with the creative freedom to design spaces that are both functional and visually striking. As the architecture sector continues to evolve, laminated glass stands out as a key component shaping the future of modern buildings.

Advantages of Laminated Glass in Energy Efficiency and Insulation
Laminated glass is becoming increasingly popular in modern architecture, particularly due to its exceptional energy efficiency and insulation properties. One of the key advantages of laminated glass is its ability to reduce energy consumption. By incorporating multiple layers, laminated glass effectively minimizes heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a building. This results in a more stable indoor climate and less reliance on heating and cooling systems, ultimately leading to lower energy bills.
In addition to its energy-saving capabilities, laminated glass also enhances insulation against sound. The interlayer between the glass sheets acts as a barrier to noise, making it an excellent choice for urban environments where sound pollution is prevalent. This contributes to a more comfortable living and working space, promoting productivity and well-being. Furthermore, laminated glass helps protect interiors from ultraviolet (UV) radiation, reducing potential damage to furniture and fabrics while maintaining a comfortable atmosphere. Overall, the advantages of laminated glass play a significant role in advancing sustainable and modern architectural design.
Top 10 Benefits of Using Laminated Glass in Modern Architecture - Advantages of Laminated Glass in Energy Efficiency and Insulation
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Energy Efficiency | Impact on Insulation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Noise Reduction | Laminated glass significantly reduces external noises, promoting a peaceful indoor environment. | Helps in maintaining a comfortable temperature, indirectly saving energy. | Enhances indoor acoustics and comfort levels. |
| UV Protection | Blocks up to 99% of harmful UV rays, protecting furnishings and minimizing skin exposure. | Reduces reliance on artificial lighting, thus saving energy. | Protects interior elements from fading and damage. |
| Safety and Security | Difficult to break, providing protection against break-ins and accidents. | Adds a layer of safety, possibly reducing energy used in lighting emergencies. | Contributes to overall building safety, enhancing insulation performance. |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces thermal transfer, leading to lower heating and cooling costs. | Directly enhances energy efficiency of buildings. | Improves thermal insulation properties. |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Available in various finishes and colors, providing design flexibility. | Potentially reduces the need for additional light sources due to better aesthetics. | Enhances overall look while aiding insulation. |
| Condensation Control | Minimizes interior condensation which can lead to mold growth. | Ensures consistent indoor climate, reducing energy requirements. | Prevents moisture issues that can impact insulation effectiveness. |
| Durability | Resists scratches and wear over time, prolonging lifespan. | Less frequent replacements contribute to energy savings in production. | Maintains insulation value longer due to reduced need for replacements. |
| Increased Property Value | Higher market appeal leading to potentially increased property values. | Efficient features can demand higher rents/sale prices. | Better insulation can be a selling point for energy-conscious buyers. |
| Reduced Glare | Laminated glass helps to lessen glare from the sun. | Leads to lesser use of window coverings and artificial lighting. | Helps in maintaining a comfortable indoor atmosphere. |
| Environmental Benefits | Sourcing can include recycled materials, contributing to sustainability. | Energy-efficient buildings reduce overall carbon footprints. | Contributes to eco-friendly building initiatives enhancing thermal management. |
Enhancing Safety and Security with Laminated Glass in Architecture
Laminated glass has become an integral component in modern architecture, particularly in enhancing safety and security. This versatile material consists of two or more sheets of glass bonded together with a layer of polymer interlayer, which not only improves structural integrity but also guards against breakage. In the event of an impact, such as a forced entry or natural disaster, the interlayer holds the glass fragments together, significantly minimizing the risk of injury and preventing unauthorized access.
In addition to its protective features, laminated glass also provides sound insulation, making it ideal for urban environments where noise pollution is a concern. The thick interlayer dampens sound transmission, creating a more peaceful indoor atmosphere. Moreover, laminated glass can be designed to include UV filtering properties, protecting both the interior furnishings and occupants from harmful sun rays. This dual functionality of safety and comfort makes laminated glass an essential element in contemporary architectural designs, catering to both aesthetic preferences and practical needs.
Aesthetic Versatility: Laminated Glass Design Options and Applications
Laminated glass offers remarkable aesthetic versatility that makes it a popular choice in modern architecture. Its ability to be customized in various colors, tints, and finishes allows architects and designers to create visually striking facades and interiors. The interlayer materials used in laminated glass, which can include anything from decorative films to printed designs, add an extra layer of creativity, enabling buildings to stand out in unique ways. This flexibility not only enhances the visual appeal of structures but also allows for seamless integration with different architectural styles, from contemporary to traditional.
In addition to its aesthetic benefits, laminated glass is ideal for various applications, including windows, skylights, and curtain walls. Its noise reduction properties and UV resistance contribute to a more comfortable indoor environment while also protecting furnishings from sun damage. Designers can experiment with transparency and translucency to create spaces filled with natural light while maintaining privacy. With such diverse design options and functional applications, laminated glass serves as an essential material in crafting innovative and appealing architectural solutions.
Noise Reduction Benefits of Laminated Glass in Urban Environments
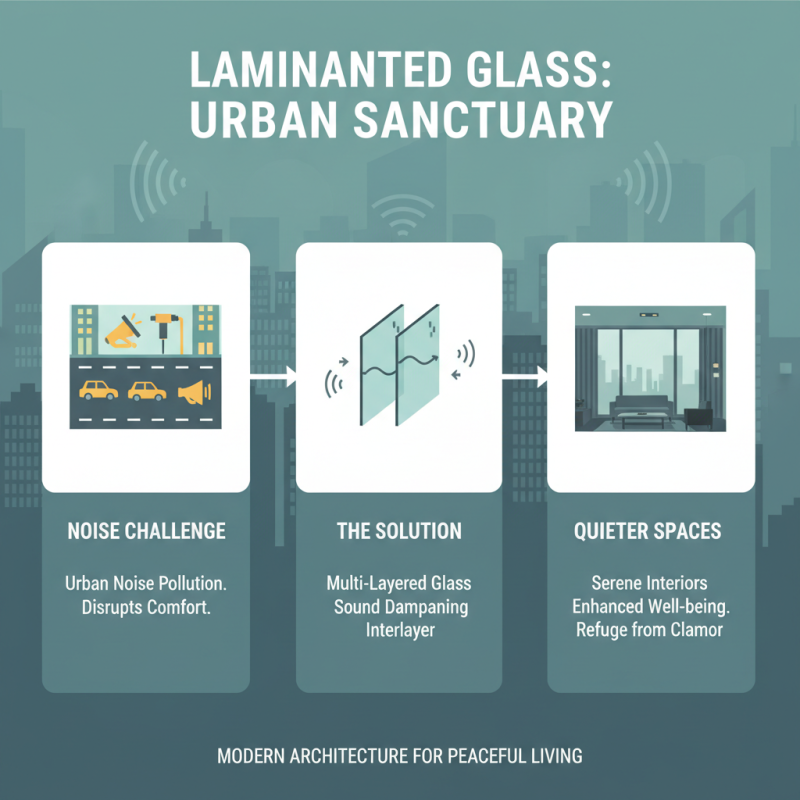
Laminated glass has become increasingly popular in modern architecture, particularly in urban environments where noise pollution is a significant concern. This type of glass consists of multiple layers of glass with an interlayer, which can effectively dampen sound waves. The result is a quieter indoor environment, enhancing the comfort of spaces in bustling cities. By using laminated glass, architects can create serene living and working spaces that provide a refuge from the clamor of street traffic, construction, and other urban noises.
When opting for laminated glass for sound reduction, consider its thickness and the type of interlayer used. Thicker glass panels generally provide better sound insulation, while specific interlayer materials can enhance acoustic performance. It's essential to work with professionals who can help select the appropriate glass based on your specific needs and the environmental noise levels of your location.
In addition, while laminated glass excels in noise reduction, it also offers other benefits such as UV protection and increased safety. By integrating this glass into your architectural designs, you can create multifunctional spaces that not only shield occupants from external noise but also promote overall well-being. As urban living continues to grow, laminated glass stands out as a smart solution for enhancing the quality of life in high-density areas.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness of Laminated Glass Materials
Laminated glass has emerged as a popular choice in modern architecture, particularly due to its sustainability and eco-friendliness. This material is composed of two or more glass sheets bonded together with an interlayer, often made from polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). One of the significant environmental benefits of laminated glass is its ability to enhance energy efficiency in buildings. By reducing heat gain and loss, laminated glass minimizes the reliance on artificial heating and cooling systems, thereby lowering energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Additionally, laminated glass contributes to sustainability by maximizing natural light without compromising safety. This material can be designed to meet various acoustic and thermal performance requirements, making it an excellent option for creating comfortable and energy-efficient spaces. The use of recycled materials in some laminated glass products further reduces its environmental impact. The durability of laminated glass also ensures longevity, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and reducing waste in landfills, aligning well with sustainable building practices.
Related Posts
-

What is Laminated Glass? Benefits, Types, and Applications Explained
-

10 Best Commercial Glass Door Options for Modern Businesses in 2023
-

Unlocking Safety and Style with Glass Handrail Systems Benefits
-

Exploring Glass Door Pulls Trends at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Enhancing Home Security: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Door Hardware
-

How to Choose the Best Sliding Glass Door Locks for Your Home Security
