How to Choose Architectural Glazing for Your Building Needs?
When selecting architectural glazing for your building, several factors come into play. Architectural glazing not only influences aesthetics but also impacts energy efficiency and comfort. The right choice can elevate a structure's visual appeal while maintaining functionality.
Consider the building's orientation and the climate. These elements affect daylighting and heat control. Some glazing options may offer better insulation, while others enhance natural light. Choosing the right type is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Also, reflect on maintenance needs. Some glass types may require more upkeep, which can lead to higher costs. It's essential to weigh these factors carefully. Your choices in architectural glazing will ultimately shape your building's experience and functionality.

Understanding the Role of Architectural Glazing in Building Design
Architectural glazing significantly influences building design. It affects aesthetics, energy efficiency, and occupant comfort. According to a report by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory, about 50% of a building's energy consumption is linked to heating, cooling, and lighting. Proper glazing can reduce this impact. Well-chosen glass can enhance natural light and reduce glare, making spaces more inviting.
However, choosing the right glazing is complex. It’s essential to consider various factors like climate and building orientation. For instance, low-E coatings can minimize heat loss in colder climates. Yet, over-reliance on glass can lead to excessive heat gain in warmer regions. A study from the American Institute of Architects indicates that up to 30% of energy waste is due to poor glazing decisions.
There is also a balance between aesthetic appeal and functionality. While large glass facades create stunning visuals, they can cause thermal discomfort. The challenge lies in aligning design aspirations with practical performance. Reflecting on your glazing choices is crucial. Exploring different materials and technologies may bring unexpected insights. This is not just an aesthetic decision; it's a fundamental aspect of sustainable design.
Types of Architectural Glazing: Pros and Cons for Different Applications
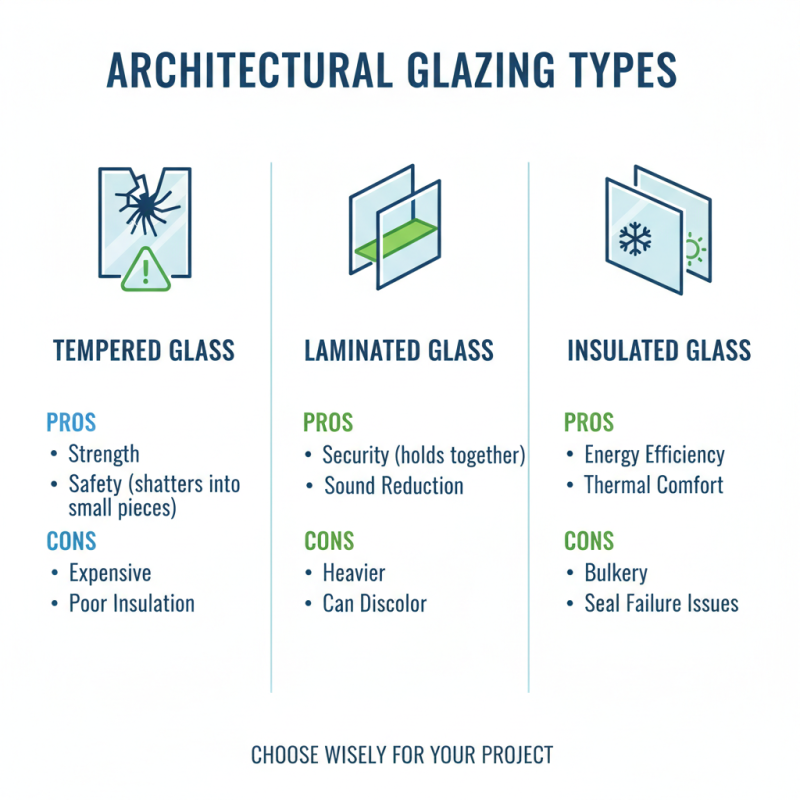
When choosing architectural glazing, understanding the types available is crucial. Common options include tempered glass, laminated glass, and insulated glass. Each type offers distinct benefits but also presents drawbacks. For instance, tempered glass is known for its strength and safety. However, it can be expensive and may not provide the best insulation.
Laminated glass combines safety and sound reduction features. This type can minimize noise pollution by up to 30%. Yet, it often has a higher initial cost. Insulated glass units (IGUs) are popular for energy efficiency, reducing heat loss by up to 30% compared to single-pane glass. Still, they may require more maintenance over time.
Architectural glazing choices can influence building performance. A report from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that high-performance glazing can reduce energy consumption by approximately 10–20%. However, the right choice is not always clear. An architect’s design concept may clash with budget limitations. It’s essential to balance aesthetics, performance, and costs.
Key Performance Criteria for Selecting Architectural Glazing
Choosing the right architectural glazing for a building can be a daunting task. Key performance criteria play a significant role in this decision-making process. One crucial aspect is energy efficiency. Opting for glazing that minimizes heat loss is essential. This helps maintain a stable internal temperature. You might also consider solar control features. These features can reduce glare and heat gain in sunny locations.
Another important factor is structural integrity. The glazing must withstand various environmental stresses. This includes wind, rain, and even seismic activity. Assessing the product’s durability is vital. Unexpected breakages can lead to costly repairs.
Aesthetics also matter. The visual appeal of a building can be enhanced with the right glazing choices. Selecting from a range of textures and colors can transform the look. However, failing to balance performance with appearance can lead to regrettable outcomes. Reviewing all these aspects carefully is crucial. It can mean the difference between successful design and future modifications.
Factors to Consider: Energy Efficiency, Aesthetics, and Durability
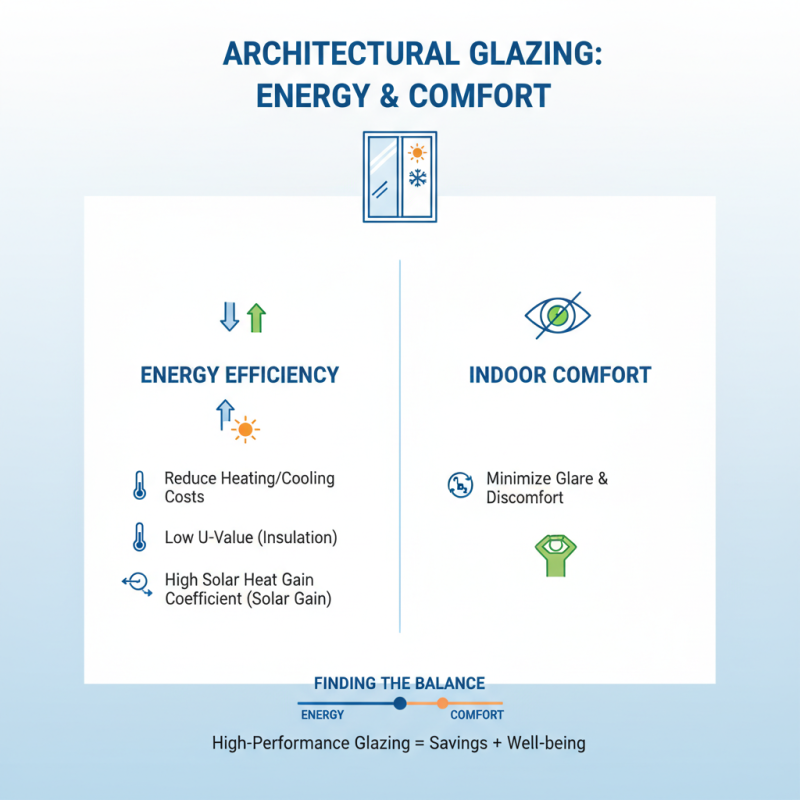
Choosing the right architectural glazing is crucial for any building project. Energy efficiency plays a significant role. High-performance glazing can reduce heating and cooling costs. Look for windows with low U-values and high solar heat gain coefficients. But striking a balance can be tricky. Too much glare can create discomfort indoors, despite energy savings.
Aesthetics is another important factor. The glazing should complement the building's design. Clear, frosted, or tinted options each offer different visual effects. However, what looks good in theory may not suit the actual environment. Local lighting conditions can change how glazing appears throughout the day.
Durability is essential too. Some materials may withstand extreme weather better than others. Yet, maintenance is an ongoing consideration. A beautiful façade can age poorly if not properly cared for. Reflect on how your choices will impact the building over time. The right glazing can enhance your project's longevity and visual appeal, but the decision requires careful thought.
Installation and Maintenance: Best Practices for Architectural Glazing
When installing architectural glazing, attention to detail is crucial. Proper alignment and support are necessary. Ensure that the frame is level before securing it in place. Inadequate support can lead to structural issues over time. Always consider potential thermal expansion. Glazing may shift with temperature changes, causing cracks or breaks. Regular inspections can help catch these problems early.
Maintenance is equally important. Clean the glass regularly to avoid buildup. A mixture of mild soap and water often works best. However, using abrasive materials can scratch the surface. Pay attention to seals and gaskets, as these can deteriorate and allow water infiltration. If you notice leaks, address them immediately. Ignoring small issues can lead to larger, costlier repairs down the line.
Reflecting on your glazing choices is key. Not every installation will perform perfectly. It’s beneficial to gather feedback and analyze any shortcomings. Understanding what works and what doesn’t will help inform future projects and enhance your skills in building design.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Glass Systems Transforming Modern Architecture and Design
-

Exploring the Top Glass Wall Systems Trends for 2025: What You Need to Know
-

How to Choose the Best Metal and Glass Doors for Your Home?
-

How to Choose the Perfect House Doors for Your Home Design Needs
-

10 Best Sliding Glass Door Systems for Modern Homes
-

How to Choose the Right Sliding Glass Door Handles for Your Home
