What is Laminated Glass? Benefits, Types, and Applications Explained
Laminated glass has emerged as a vital material in modern architecture and construction, known for its unique combination of safety, strength, and aesthetic appeal. John Smith, a renowned expert in the laminated glass industry, notes, "The versatility of laminated glass not only enhances structural integrity but also provides unmatched safety and sound insulation." This multifaceted material consists of two or more glass panes bonded together with an interlayer, usually made from polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). As a result, laminated glass offers numerous benefits ranging from enhanced protection against impact to improved thermal efficiency.
The applications of laminated glass are vast, making it suitable for diverse settings, including residential buildings, commercial establishments, and vehicles. Its ability to maintain its form even when shattered ensures that it serves both functional and decorative purposes. With increasing awareness of energy efficiency and safety standards, laminated glass is becoming the material of choice for architects and builders aiming to combine beauty with performance. As we delve deeper into the benefits, types, and applications of laminated glass, it becomes clear that this innovative solution is shaping the future of construction and design.
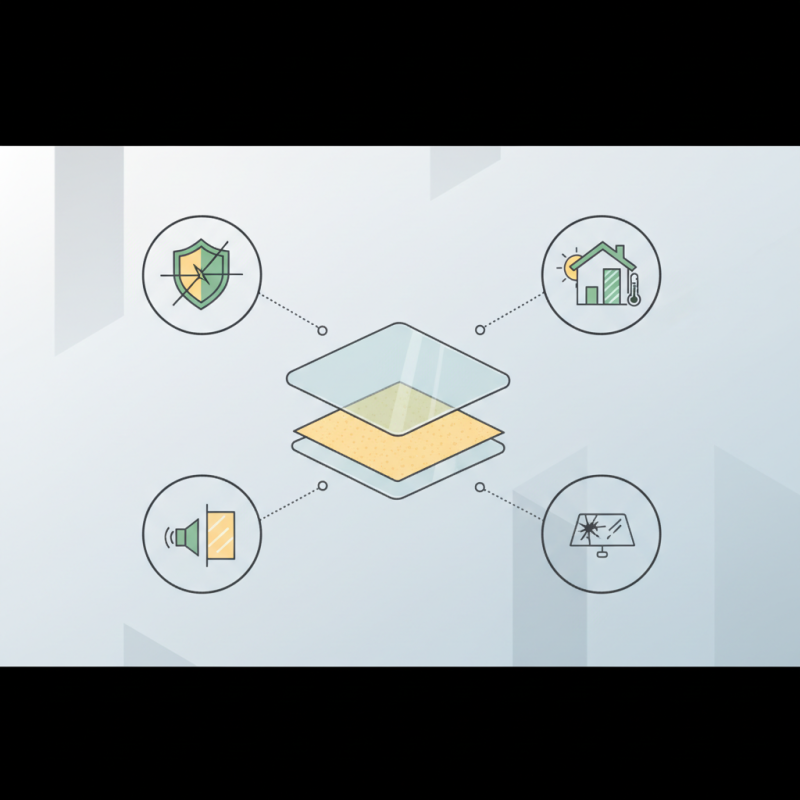
What is Laminated Glass?
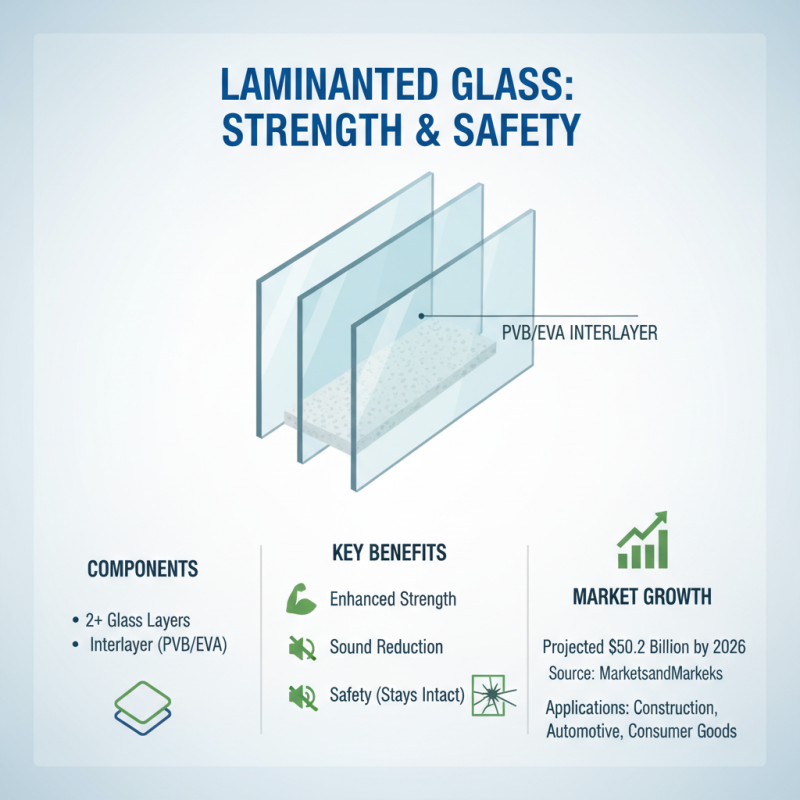
Laminated glass is a type of safety glass that consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). This interlayer provides enhanced strength, reduces sound transmission, and holds the glass layers together in the event of breakage, making it less likely to shatter. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global laminated glass market is projected to reach $50.2 billion by 2026, highlighting its increasing popularity across various sectors including construction, automotive, and consumer goods.
Tip: When considering laminated glass for a project, evaluate the specific sound insulation requirements. Different interlayer materials can significantly affect the sound attenuation performance of the laminated glass.
The versatility of laminated glass extends its application beyond safety. In architecture, it can be used for decorative purposes, offering aesthetic benefits without compromising security. Additionally, it provides UV protection, blocking up to 99% of harmful UV rays, which can help preserve interiors and reduce fading in furniture and artworks. As the demand for energy-efficient building materials rises, laminated glass stands out for its functional qualities, particularly in passive solar design strategies.
Tip: Always consult with a professional when selecting laminated glass to ensure it meets local building codes and is appropriate for your specific application needs.
Key Benefits of Using Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is gaining popularity in various sectors due to its exceptional benefits. One of the key advantages is its enhanced safety. According to the National Glass Association, laminated glass is created by bonding two or more glass layers with an interlayer, typically made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This construction provides high resistance to breaking, which not only protects against accidental injuries from glass fragments but also acts as a deterrent against break-ins, making it an ideal choice for homes and commercial buildings.
Another significant benefit of laminated glass is its sound attenuation properties. The interlayer effectively dampens sound, resulting in a peaceful indoor environment. A report by the Acoustic Society of America states that laminated glass can reduce sound transmission by up to 50%, which is particularly beneficial for buildings located in noisy urban areas or near highways.
Tips: When selecting laminated glass for a project, consider the local climate and application needs. Higher interlayer thickness can enhance security and sound insulation, while tinted or frosted laminates can provide additional privacy. Always consult with a glass professional to determine the ideal specifications that align with your requirements.
Different Types of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass is known for its unique composition, which includes two or more layers of glass bonded together with an interlayer, often made of polyvinyl butyral (PVB). This design increases safety and enhances sound insulation. Different types of laminated glass serve various purposes, tailored to meet specific needs in architecture, automotive, and other industries.
One common type is the safety laminated glass, which is specifically designed for situations where there's a risk of breakage. It prevents shattering by keeping the glass pieces adhered to the interlayer upon impact. Another variant is acoustic laminated glass, which features a thicker interlayer to significantly reduce sound transmission, making it ideal for buildings located in noisy environments. Additionally, there are UV-filtering laminated glasses, which not only provide safety but also protect interiors from harmful ultraviolet rays. Each type of laminated glass offers distinct benefits, making it a versatile choice for both aesthetic and functional applications.
What is Laminated Glass? Benefits, Types, and Applications Explained
| Type of Laminated Glass | Benefits | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Laminated Glass | Improved safety, reduces noise | Windows, doors, and skylights |
| Acoustic Laminated Glass | Excellent sound insulation | Concert halls, offices, and residences |
| Security Laminated Glass | High impact resistance | Banks, jewelry stores, and safety partitions |
| Bullet Resistant Laminated Glass | Prevents penetration from bullets | Government buildings, military installations |
| Solar-Control Laminated Glass | Reduces solar heat gain | Office buildings, commercial spaces |
Common Applications of Laminated Glass
Laminated glass has gained substantial traction across various industries due to its unique properties and benefits. Commonly used in the construction sector, laminated glass is prevalent in skylights, facades, and windows for both residential and commercial buildings. Its ability to hold together when shattered not only enhances safety but also improves sound insulation, making it a favorable choice for urban environments. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global laminated glass market is projected to reach USD 34.79 billion by 2025, reflecting the growing demand stemming from these applications.
In the automotive industry, laminated glass is increasingly being utilized in windshields and sunroofs. This application ensures passenger safety by minimizing the risk of injury from shattered glass fragments during accidents. The rise in consumer awareness regarding safety features has driven the automotive laminated glass market, with an expected CAGR of 6.4% from 2020 to 2025, as reported by ResearchAndMarkets. Furthermore, laminated glass finds its way into various specialized fields, such as bullet-resistant glass for security applications and soundproof glass for recording studios, highlighting its versatility and adaptability across different environments.
Maintenance and Care for Laminated Glass
Maintaining laminated glass is essential for ensuring its longevity and aesthetic appeal. Regular cleaning is the first step in proper care. Use a soft, lint-free cloth and a gentle glass cleaner to wipe the surface. Avoid abrasive materials or harsh chemicals, as they can scratch the glass or damage the interlayer. For best results, clean the glass regularly to prevent the buildup of dirt and grime, which can affect visibility and appearance.
In addition to cleaning, inspecting laminated glass for any signs of wear or damage is crucial. Look for cracks, chips, or delamination, as these issues can compromise the glass's integrity. If you notice any problems, it’s advisable to consult a professional for assessment and potential repairs. It’s also beneficial to ensure that the frames and seals surrounding the laminated glass are in good condition, as these components play a significant role in maintaining the glass’s performance and energy efficiency. By following these maintenance tips, you can help extend the life of your laminated glass and keep it looking great.
Related Posts
-

The Impact of Storefront Glass Doors on Retail Aesthetics and Consumer Behavior
-

Choosing the Right Entry Door Hardware for Enhanced Home Security and Style
-

How to Choose the Best Glass Wall Systems for Your Modern Space in 2025
-

How to Select the Right Glass Door Hardware for Your Home Design
-

Enhancing Home Security: The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Door Hardware
-

How to Choose the Best Aluminum Doors for Your Home Upgrade
